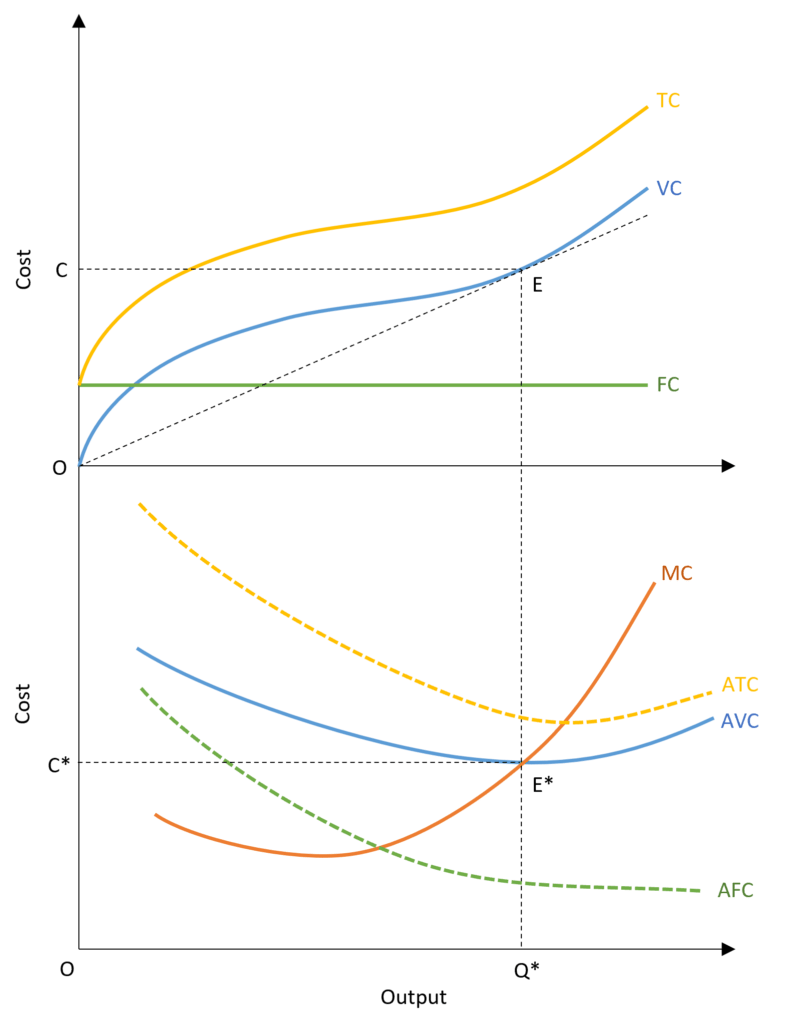
Explain Short Run Cost Curve . Fixed cost, variable cost, total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost. The cost function is a functional relationship between cost and output. The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the. We’ve explained that a firm’s. In the short run, capital is fixed. Describe the relationship between production and costs, including average and marginal costs. Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of diminishing returns. It explains that the cost of. We calculate average total cost (atc) by dividing total cost by the total quantity produced. There are seven cost curves in the short run: Our analysis of production and cost begins with a period economists call the short run. The fixed cost ( f c f c). In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. After a certain point, increasing extra workers leads. In a free market economy,.
from spureconomics.com
The cost function is a functional relationship between cost and output. Describe the relationship between production and costs, including average and marginal costs. The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the. We’ve explained that a firm’s. The fixed cost ( f c f c). Our analysis of production and cost begins with a period economists call the short run. Fixed cost, variable cost, total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost. Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of diminishing returns. After a certain point, increasing extra workers leads. It explains that the cost of.
Shortrun Costs Total, Average and Marginal Costs
Explain Short Run Cost Curve Our analysis of production and cost begins with a period economists call the short run. The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the. In the short run, capital is fixed. The fixed cost ( f c f c). In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of diminishing returns. After a certain point, increasing extra workers leads. We’ve explained that a firm’s. In a free market economy,. There are seven cost curves in the short run: Our analysis of production and cost begins with a period economists call the short run. It explains that the cost of. Describe the relationship between production and costs, including average and marginal costs. The cost function is a functional relationship between cost and output. Fixed cost, variable cost, total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost. We calculate average total cost (atc) by dividing total cost by the total quantity produced.
From studylib.net
Short Run and Long Run Average Cost Curves Relationship and Difference Explain Short Run Cost Curve The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the. It explains that the cost of. In a free market economy,. We’ve explained that a firm’s. After a certain point, increasing extra workers leads. The cost function is a functional relationship between cost and output. Describe the relationship between production and costs, including average and marginal. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From www.coursehero.com
Each graph illustrates three shortrun cost curves for firms, where Explain Short Run Cost Curve Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of diminishing returns. We calculate average total cost (atc) by dividing total cost by the total quantity produced. The cost function is a functional relationship between cost and output. The fixed cost ( f c f c). Fixed cost, variable cost, total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, average. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From www.chegg.com
Solved The graph below represents the shortrun cost curves Explain Short Run Cost Curve It explains that the cost of. The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the. We’ve explained that a firm’s. We calculate average total cost (atc) by dividing total cost by the total quantity produced. There are seven cost curves in the short run: In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From www.youtube.com
Shortrun and longrun cost curves Theory of Cost UGC NET JRF Explain Short Run Cost Curve The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the. Fixed cost, variable cost, total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost. The fixed cost ( f c f c). There are seven cost curves in the short run: Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Rittenberg Chapter 8 Production and Cost PowerPoint Presentation Explain Short Run Cost Curve After a certain point, increasing extra workers leads. In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. Our analysis of production and cost begins with a period economists call the short run. In the short run, capital is fixed. The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From open.lib.umn.edu
8.1 Production Choices and Costs The Short Run Principles of Economics Explain Short Run Cost Curve Our analysis of production and cost begins with a period economists call the short run. Describe the relationship between production and costs, including average and marginal costs. The cost function is a functional relationship between cost and output. The fixed cost ( f c f c). The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the.. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From www.youtube.com
Short run Cost curve Total Variable Cost (With Numerical Example Explain Short Run Cost Curve In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. Describe the relationship between production and costs, including average and marginal costs. The fixed cost ( f c f c). In the short run, capital is fixed. Fixed cost, variable cost, total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, average. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 8 Production and Cost in the Short Run PowerPoint Explain Short Run Cost Curve In the short run, capital is fixed. The fixed cost ( f c f c). There are seven cost curves in the short run: Fixed cost, variable cost, total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost. Describe the relationship between production and costs, including average and marginal costs. We calculate average total cost (atc). Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From www.transtutors.com
(Solved) When Production Costs Rise, A. The ShortRun Aggregate Explain Short Run Cost Curve It explains that the cost of. Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of diminishing returns. In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. We calculate average total cost (atc) by dividing total cost by the total quantity produced. The short run in this microeconomic. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From arinjayacademy.com
Short Run Cost in Economics Class 11 Notes Microeconomics Explain Short Run Cost Curve There are seven cost curves in the short run: Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of diminishing returns. We’ve explained that a firm’s. Our analysis of production and cost begins with a period economists call the short run. It explains that the cost of. In a free market economy,. Fixed cost, variable cost, total cost, average. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From spureconomics.com
Shortrun Costs Total, Average and Marginal Costs Explain Short Run Cost Curve The fixed cost ( f c f c). Describe the relationship between production and costs, including average and marginal costs. Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of diminishing returns. There are seven cost curves in the short run: The cost function is a functional relationship between cost and output. In a free market economy,. In economics,. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From www.intelligenteconomist.com
Perfect Competition Short Run Intelligent Economist Explain Short Run Cost Curve In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. In the short run, capital is fixed. After a certain point, increasing extra workers leads. The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the. Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From www.tutor2u.net
Perfect Competition Short Run Price and Output Economics tutor2u Explain Short Run Cost Curve The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the. It explains that the cost of. In the short run, capital is fixed. We calculate average total cost (atc) by dividing total cost by the total quantity produced. The fixed cost ( f c f c). After a certain point, increasing extra workers leads. The cost. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Relationship between longrun & shortrun average cost curves Explain Short Run Cost Curve The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the. Fixed cost, variable cost, total cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, average total cost, and marginal cost. The fixed cost ( f c f c). In a free market economy,. In economics, a cost curve is a graph of the costs of production as a. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From present5.com
1 Output and Costs CHAPTER 11 2 After Explain Short Run Cost Curve Describe the relationship between production and costs, including average and marginal costs. It explains that the cost of. In the short run, capital is fixed. In a free market economy,. We calculate average total cost (atc) by dividing total cost by the total quantity produced. Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of diminishing returns. The cost. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Figure ShortRun Costs Cost curves (dollars) 200 Explain Short Run Cost Curve There are seven cost curves in the short run: In a free market economy,. After a certain point, increasing extra workers leads. The fixed cost ( f c f c). The cost function is a functional relationship between cost and output. In the short run, capital is fixed. Our analysis of production and cost begins with a period economists call. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From www.bartleby.com
ShortRun Costs and LongRun Costs bartleby Explain Short Run Cost Curve The fixed cost ( f c f c). In a free market economy,. It explains that the cost of. Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of diminishing returns. We calculate average total cost (atc) by dividing total cost by the total quantity produced. After a certain point, increasing extra workers leads. In the short run, capital. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.
From hubpages.com
ShortRun Average and Marginal Cost Curves HubPages Explain Short Run Cost Curve The short run in this microeconomic context is a planning period over which the. In a free market economy,. It explains that the cost of. After a certain point, increasing extra workers leads. We’ve explained that a firm’s. Short run cost curves tend to be u shaped because of diminishing returns. We calculate average total cost (atc) by dividing total. Explain Short Run Cost Curve.